How Does It Work
Geophones
Compilation of ground motion measurements
Geophones
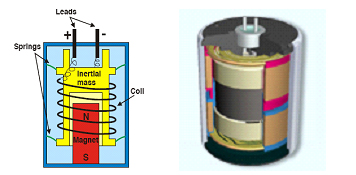
When the geophone case is accelerated, the sensing
coil moves with respect to the fixed magnet. The
gradient of the magnetic field transforms the relative
velocity into an emf (with sensitivity G), which can
then be put in series with a load resistor Rd to produce
a measurable voltage. The flowing current I generates
a linear force, opposite to the direction of motion, that
provides a strong mechanical damping effect.
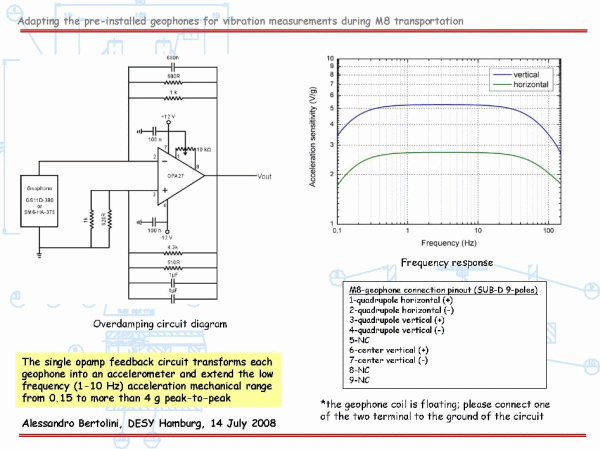
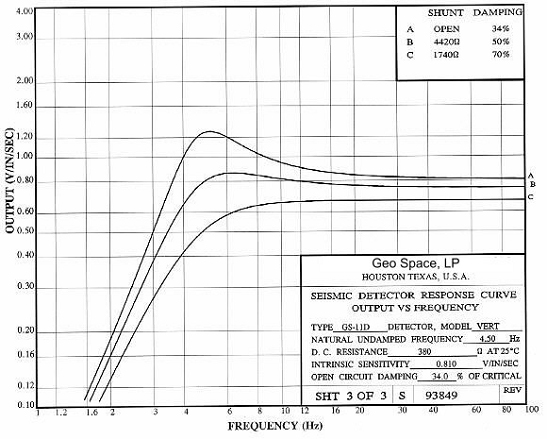
Frequency response
The frequency response of output voltage vs case/ground
velocity is determined by the sensor mechanics and by
the load/damping resistor.
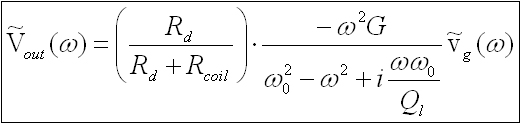
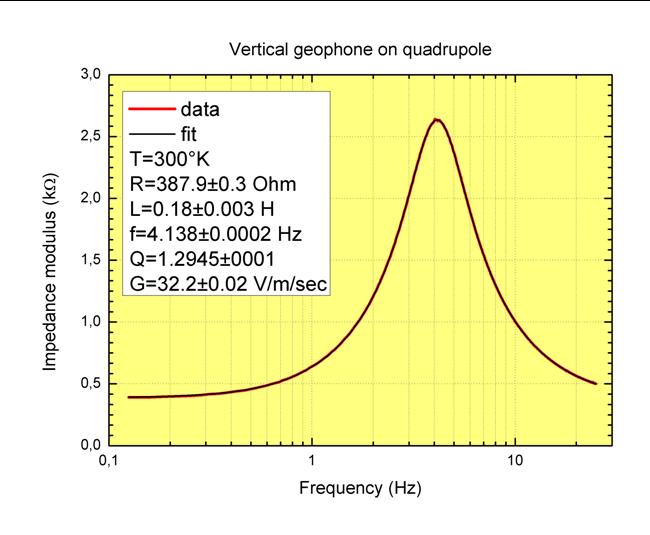
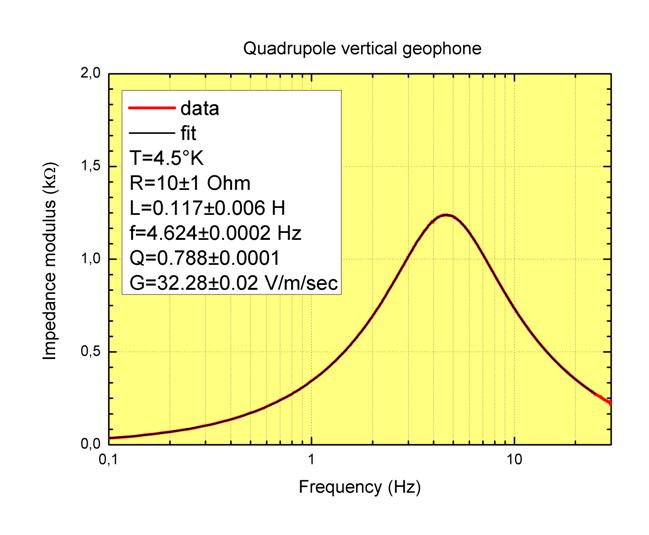
In-situ calibration method (Cold Measurement)
Accurate remote calibration possible using the signal cable
itself; no access to the sensor is necessary. By measuring
the electrical impedance vs frequency at the output
terminals of the sensor we have access to both electrical
and mechanical parameters. Only the suspended mass has
to be known.
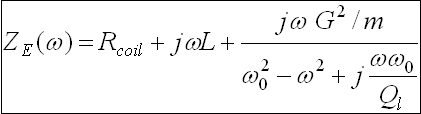
Geophone equivalent impedance
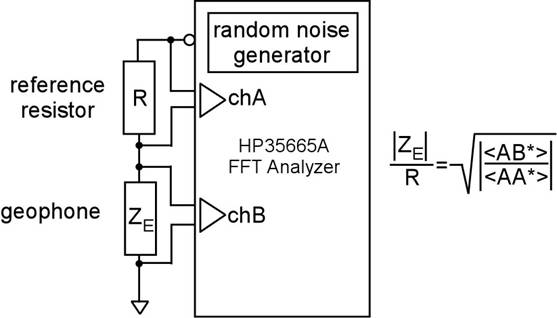
Block diagram of the calibration procedure